By Ethan Griffiths, Open Justice multimedia journalist, Te Moana-a-Toi
More than 150 Ministry of Justice staff and contractors tasked with maintaining the integrity of New Zealand's justice system faced employment action after being caught snooping through court records.
But it was two years before employment action was taken against some of those staff - almost all of whom kept their jobs.
The incidents are among more than 1500 recorded privacy breaches since 2015.
While the ministry said the breaches were "not indicative of any embedded breaches" within the country's justice system, it accepted they were "disappointing".
Chief operating officer Carl Crafar said staff were expected to uphold the integrity of the justice system.
"Any privacy breach is disappointing. Ministry staff have appropriate access based on their roles and are expected to maintain the integrity of the courts and tribunals."
Acting Privacy Commissioner Liz MacPherson told Open Justice all "serious" breaches must be reported to the Commissioner within 72 hours.
She said the numbers were higher than she was aware of - but they might not have all reached the threshold for reporting.
"We will contact the ministry for further information to confirm if any of these breaches were above the serious harm threshold and should therefore have been notified."
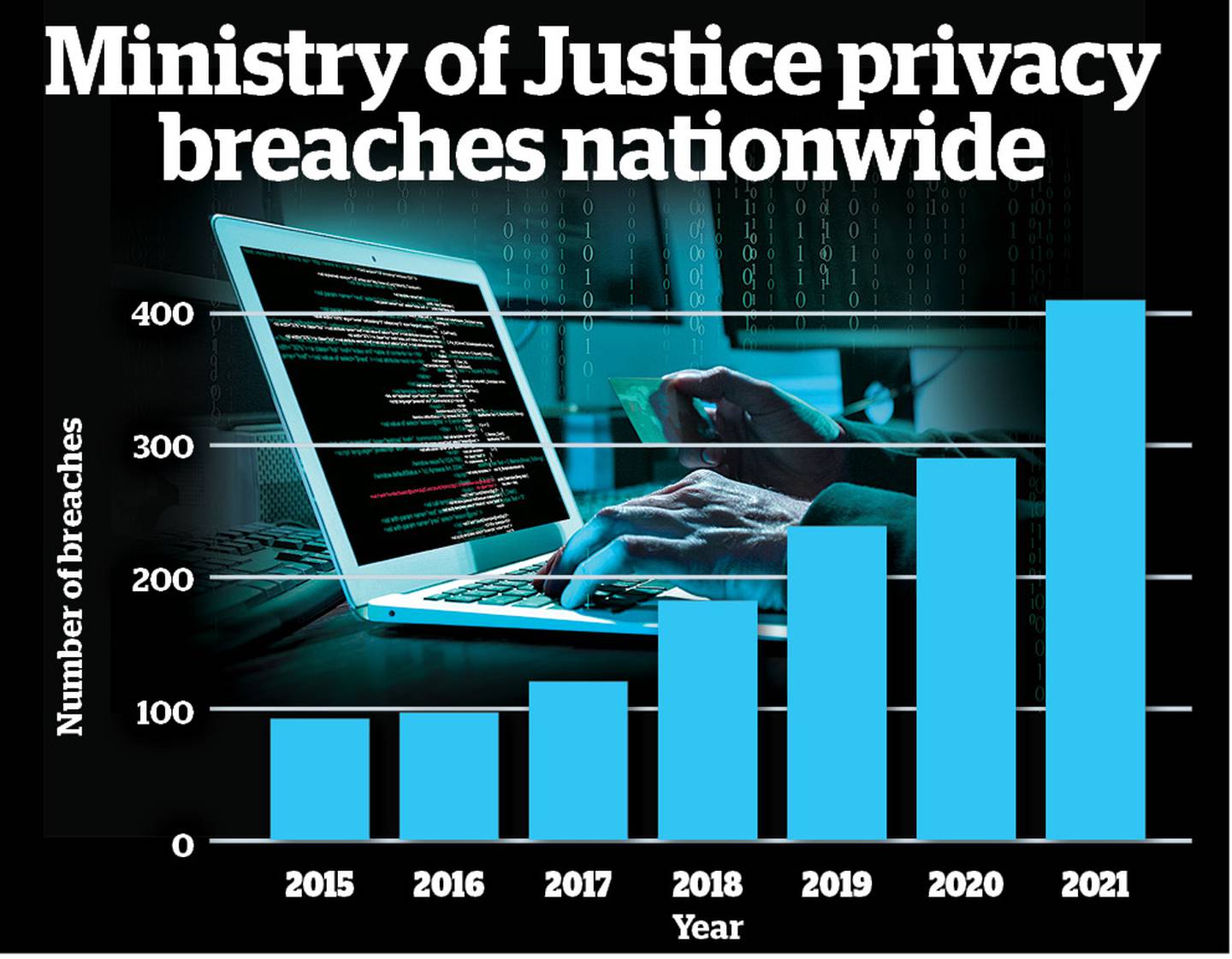
Privacy breaches by Ministry of Justice staff between 2015 and 2021 / Open Justice
According to the figures, obtained by Open Justice under the Official Information Act, 150 staff were formally warned and a single additional staffer was dismissed in the six years from 2015 to 2021.
All 151 of those employment actions were the result of staff members looking through court records without a justified reason.
They also all happened in 2020. Outside of that year, there was not a single employment action taken against a staff member.
The ministry said the employment investigations came after concerns were raised about staff accessing documents they shouldn't be.
While the breaches occurred in 2018 and 2019, it wasn't until 2020 that action was taken following the completion of employment investigations.
Asked why it took so long for that action to be taken, Crafar said it took time to carry out the process properly.
Questions remain over why there was employment action against 151 staff in one year but none in any of the other years.
The ministry strongly denied any suggestion that lax breach-monitoring processes were the reason no action was taken in the other five years.
"Our information security policies meet the government standard."
1500 privacy breaches in six years
Of the 1537 occasions where sensitive personal and criminal information held by the ministry was breached, 1225 times were by the ministry's own staff, and 220 by third-party contractors.
Just over 400 of those breaches occurred last year alone - four times the number of breaches in 2015.
Most of the breaches happened in the Wellington region, home to New Zealand's senior judiciary as well as the Supreme Court and Court of Appeal.
Auckland followed closely behind - again likely explained by the region's substantial caseload.
But the data also identified those areas where privacy breaches were higher than their caseload would suggest, such as the Ministry's offices in Tauranga which alone had more breaches than the entire Canterbury, Waikato, and Otago regions.
The Tauranga District Court and public defence service offices saw 34 total breaches. The wider Bay of Plenty region recorded the third-highest number of breaches after Wellington and Auckland, sitting at 64.
A total of 256 of the nationwide breaches did not have a location recorded while an extra 175 breaches occurred at a non-Ministry location.
Ministry's staff the 'biggest risk' - professor
Auckland University associate professor in commercial law Gehan Gunasekara, who also serves as the chair of the Privacy Foundation, told Open Justice breaches among the ministry's own staff were always the biggest risk for an agency of that size.
"I would think that's massive; that's the Trojan horse, your biggest risk," the professor said. "You want to make sure you've got trustworthy people on the inside."
"It would be disappointing if Ministry of Justice officials were essentially not following the law."
About 2700 ministry staff work in or around courts and tribunals. The ministry would not confirm how many of those staff have access to court documents through their roles.
Gunasekara said the increase in privacy breaches in recent years might be related to a change in the Privacy Act, which now requires all serious breaches to be reported almost immediately.
MacPherson said there was a misconception that privacy breaches only occurred where personal information was inadvertently shared to, or inappropriately accessed by, someone external to the agency.
"That's not the case. Internal issues such as employees looking up other people's personal records without good reason are also privacy breaches."
Crafar said the organisation had since taken steps to review its processes and introduce further prevention strategies, regular training and reminding staff of the code of conduct.
"Data security and privacy are central to our work at the Ministry of Justice and all staff receive training on the importance of safeguarding personal information."


